Introduction to 3D Printing
In recent years, 3D printing has revolutionized the way we create, offering unprecedented versatility and efficiency in various industries. From rapid prototyping to custom manufacturing, 3D printing provides a cost-effective and highly customizable method of production. However, for beginners, the world of 3D printing can be daunting, involving more than just owning a printer and filament.
This comprehensive guide aims to empower individuals and businesses interested in exploring 3D printing by providing essential insights into the supplies, materials, considerations, and costs associated with this exciting technology. By the end of this guide, readers will have a thorough understanding of what it takes to harness the full potential of 3D printing and unlock endless creative possibilities.
Understanding the Basics
Essential 3D Printer Supplies
Embarking on your 3D printing journey starts with acquiring a suitable 3D printer. The market offers a diverse range of 3D printers, each employing different technologies and catering to specific needs. Here’s an overview of the most common types:
- Stereolithography (SLA): SLA printers use ultraviolet light to cure liquid resin layer by layer, resulting in highly detailed prints with smooth surfaces. These printers are known for their accuracy and are commonly used for creating prototypes and small-scale models.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM printers extrude melted plastic filament through a nozzle, building objects layer by layer. They are widely used due to their affordability, ease of use, and ability to print with a variety of materials. FDM printers are versatile and suitable for both hobbyists and professionals.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): DLP printers use digital light projectors to cure liquid resin, similar to SLA printers. They offer faster printing speeds and higher resolutions, making them ideal for producing detailed models and prototypes.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): SLS printers use a laser to fuse powdered materials, such as nylon or polyamide, layer by layer. This technology allows for printing complex geometries and functional prototypes with excellent durability.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): DMLS printers use a high-powered laser to fuse metal powders, creating solid metal objects. This process enables the production of highly durable and precise metal parts, making it ideal for aerospace and industrial applications.

In addition to selecting the right type of 3 printer, there are several essential supplies and accessories that you’ll need to ensure a seamless printing experience:
- Storage Containers: Proper storage is crucial to maintain the integrity of your printing materials. Airtight containers help keep filaments and resins fresh and prevent moisture absorption, which can compromise print quality.
- Adhesives: Adhesives are necessary to secure your prints to the build plate, ensuring they don’t shift or become detached during the printing process. Common adhesives include glue sticks, hairspray, and specialized 3D printing bed adhesives.
- Build Plates: Build plates provide a flat, stable surface for your prints to adhere to. Different materials, such as glass, aluminum, or heated build plates, are available, each offering unique advantages in terms of adhesion and surface finish.
- Ventilation Equipment: 3D printing can generate fumes and odors, depending on the materials used. Proper ventilation is essential to maintain a safe printing environment and mitigate potential health hazards. Consider investing in an air purifier or setting up a dedicated ventilation system for your printing space.
- Precision Tools: Calipers and micrometers are indispensable for measuring the accuracy and precision of your prints. These tools help ensure that your printed objects meet the desired specifications and dimensional accuracy.
- Maintenance Toolset: 3D printers require regular maintenance and occasional repairs. A basic toolset, including screwdrivers, wrenches, and cleaning tools, is essential for keeping your printer in optimal condition.
Exploring the World of Printing Materials

The choice of printing material significantly impacts the outcome of your 3D printing projects. Each material has unique properties, affecting the strength, flexibility, durability, and aesthetic of your printed objects. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the most common printing materials:
- Plastics: Plastics are the most widely used printing materials due to their affordability, versatility, and ease of use.
- Polylactic Acid (PLA): PLA is a biodegradable plastic derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugar cane. It is user-friendly, offering good dimensional accuracy and a smooth finish. PLA is suitable for a wide range of applications, from prototypes to consumer products.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a durable and impact-resistant plastic commonly used in consumer goods, toys, and electronic enclosures. It offers high strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
- Powders: Powder-based materials are used in technologies like SLS and binder jetting. They offer unique advantages in terms of strength and flexibility, enabling intricate designs and industrial applications.
- Polyamide (Nylon): Nylon powder is known for its durability, flexibility, and impact resistance. It is often used for printing functional prototypes, tools, and end-use parts in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
- Alumide: Alumide is a composite material made from a blend of aluminum and nylon powders. It offers a metallic appearance and provides high strength and stiffness, making it suitable for structural components and durable prototypes.
- Resins: Resins are used in SLA and DLP printers, providing exceptional detail and smooth surfaces.
- Standard Resins: Standard resins are versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications. They offer high accuracy, making them ideal for small-scale models, miniatures, and detailed prototypes.
- Specialty Resins: Specialty resins are designed for specific applications, offering unique properties such as flexibility, high temperature resistance, or clear transparency.
- Metals: Metal 3D printing, facilitated by technologies like DMLS, enables the creation of highly durable and precise metal parts.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and strength, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial and engineering applications.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is lightweight, durable, and widely used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics industries.
- Titanium: Titanium provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for medical implants, aerospace components, and high-performance automotive parts.
- Composite Materials: Composite materials combine two or more materials to enhance specific properties.
- Carbon Fiber: Carbon fiber-reinforced plastics offer exceptional strength and stiffness, making them ideal for structural components in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment industries.
- Graphene: Graphene-enhanced materials provide improved thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties, opening up possibilities for advanced electronics and high-performance applications.
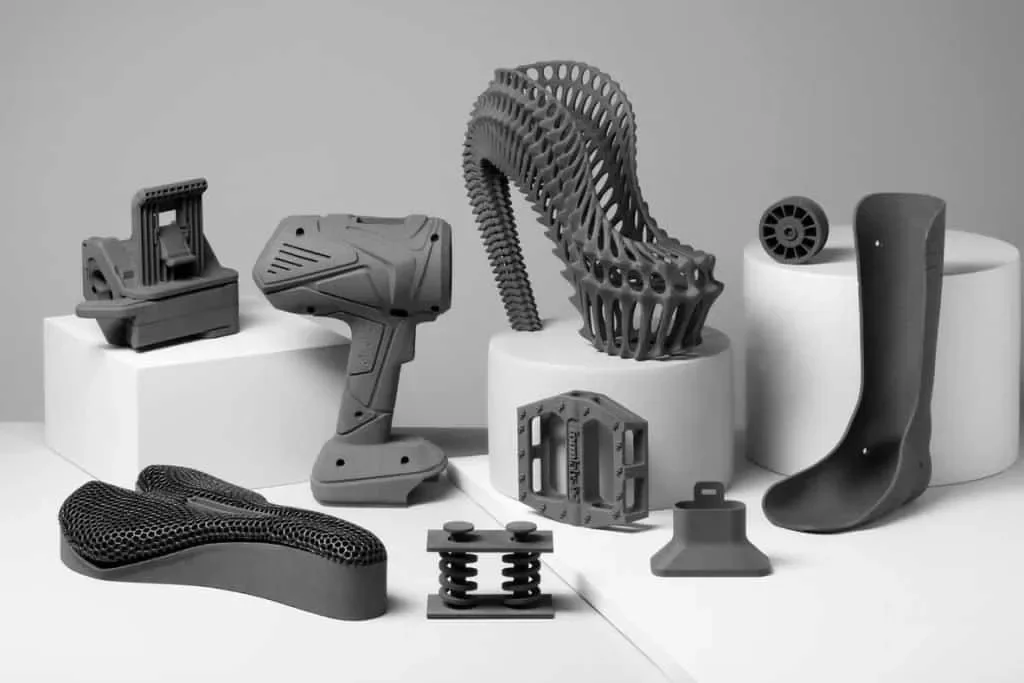

Considerations and Costs of 3D Printing
While 3D printing offers cost-saving opportunities, particularly in prototyping and small-batch production, it’s important to consider the various expenses involved. Here’s an overview of the factors contributing to the overall cost of 3D printing:
- Printer Cost: The initial investment in a 3D printer can vary significantly depending on the technology, brand, and features. Consumer-grade FDM printers can range from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars, while industrial-grade printers, such as SLS or DMLS machines, can cost tens of thousands or even hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Printing Materials: The choice of printing material directly impacts the cost of your projects. Plastic filaments, such as PLA and ABS, are generally affordable, with prices ranging from $20 to $50 per kilogram. However, specialty materials, such as metal powders or carbon fiber-infused filaments, can be significantly more expensive, often costing several hundred dollars per kilogram.
- Accessories and Maintenance: The cost of essential accessories, such as build plates, adhesives, and precision tools, should be factored into your budget. Additionally, regular maintenance and replacement of printer components, such as nozzles or print beds, will incur further expenses.
- Post-Processing: Depending on the printing technology and material used, post-processing may be required to finish your printed objects. This can include support removal, sanding, painting, or additional surface treatments, adding to the overall cost.
- Power Consumption: 3D printers consume varying amounts of electricity, depending on their size, technology, and usage. Consider the ongoing cost of electricity, especially for industrial-grade printers or when operating multiple printers simultaneously.
- Labor: While 3D printing can automate certain aspects of production, skilled labor is still required for design, setup, monitoring, and post-processing. The cost of labor will depend on the complexity of the project and the level of expertise needed.
- Overhead Costs: If you’re running a 3D printing business or service, don’t forget to include overhead costs, such as rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative expenses. These costs can significantly impact the overall profitability of your 3D printing endeavors.
Unlocking the Full Potential of 3D Printing
In conclusion, 3D printing offers a realm of endless possibilities, empowering individuals and businesses to bring their ideas to life. However, to harness the full potential of this exciting technology, it is crucial to approach it with a comprehensive understanding of the supplies, materials, and considerations involved.
By investing in the right equipment, selecting suitable printing materials, and carefully planning for the associated costs, you can unlock the doors to creativity, innovation, and efficient manufacturing. Whether you’re a hobbyist, entrepreneur, or established business, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the way you create, enabling you to turn your visions into reality.
As you embark on your 3D printing journey, stay curious, explore the latest advancements, and continuously seek ways to maximize the benefits that this versatile technology has to offer. With the right knowledge and tools, the possibilities are truly limitless.
